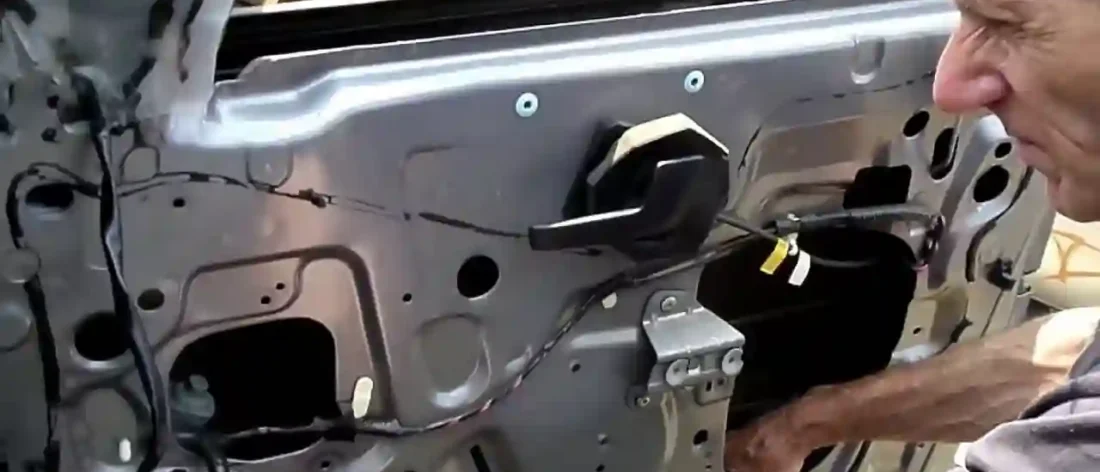
When you press a button or turn a crank to open or close your car’s window, you might not think much about the intricate mechanisms at work behind the scenes. However, the operation of your vehicle’s window regulator is a fascinating feat of engineering and science. In this article, we’ll delve into the science behind window regulator operation, exploring the principles of mechanics, electrical systems, and the role of materials that make this everyday convenience possible.
The Basics of Window Regulators:
To understand the science behind window regulator operation, let’s start with the basics. A window regulator is a device that controls the movement of a vehicle’s windows. Whether it’s manually operated through a hand crank or power-assisted with the push of a button, window regulators use mechanical and sometimes electrical systems to move the window glass up and down.
Mechanical Principles:
The mechanical aspect of window regulator operation is based on fundamental principles of mechanics, including:
- Leverage: The window regulator uses leverage to convert a relatively small amount of input force, whether from a hand crank or an electric motor, into a more significant force capable of moving the window glass. This leverage amplifies the force applied by the operator.
- Gears and Pulleys: Many window regulators incorporate gears and pulleys into their design. Gears help to transfer rotational motion efficiently, while pulleys guide and route cables or other mechanical elements, allowing for smooth and controlled movement.
- Cables and Linkages: In power window systems, cables or linkages transmit the force generated by the motor to the window glass. These components are carefully designed to provide the necessary strength and durability while ensuring precise control of the window’s position.
Electrical Systems:
In vehicles with power windows, electrical systems play a crucial role in window regulator operation. Here’s how these systems work:
- Switches and Control Modules: When you press the window switch in your vehicle, it sends an electrical signal to a control module or relay. This module determines the desired window operation (e.g., open or close) and activates the corresponding motor.
- Electric Motors: Electric motors are at the heart of power window operation. They convert electrical energy into mechanical motion, which is then transmitted to the window regulator mechanism. Reversible electric motors allow the window to move in both directions.
- Wiring and Circuits: A complex network of wiring and electrical circuits connects the switches, control modules, and motors. These circuits must be designed to handle the necessary voltage and current while ensuring safety and reliability.
- Safety Features: Many modern vehicles include safety features in their power window systems, such as sensors that detect obstructions in the window’s path. If an obstruction is detected, the motor’s operation is reversed to prevent injury or damage.
Materials and Durability:
The science behind window regulator operation also extends to materials and durability considerations:
- Material Selection: Window regulators are typically made from robust materials like steel, aluminum, or high-strength plastics. The choice of materials depends on factors such as strength, weight, and corrosion resistance.
- Friction Reduction: Lubrication plays a critical role in reducing friction and wear in window regulator mechanisms. Lubricants are carefully chosen to withstand the operating conditions and temperature extremes inside a vehicle door.
- Durable Components: Window regulator components must be designed to withstand millions of cycles over the lifespan of a vehicle. This requires precision engineering and materials that resist wear and fatigue.
- Sealing: The interior of a car door is subject to moisture and dust. Sealing is essential to protect the window regulator’s mechanical and electrical components from environmental factors that could lead to corrosion or malfunction.
Power Window Operation: A Step-by-Step Process:
Now, let’s walk through the step-by-step process of how power windows work, highlighting the science at each stage:
- Input from the Switch: When you press the window switch, it sends an electrical signal to the control module. This input is a form of electrical energy, which will be converted into mechanical energy to move the window.
- Control Module Decision: The control module receives the input and decides whether to open or close the window. It then sends a signal to the electric motor to initiate the desired action.
- Electric Motor Activation: The electric motor receives the electrical signal, which causes it to generate mechanical motion. This motion is achieved through the principles of electromagnetic force and the interaction between magnetic fields and conductive wires within the motor.
- Conversion to Mechanical Energy: The motor’s mechanical motion is transmitted to the window regulator mechanism. Gears and linkages play a crucial role in transforming the rotational motion of the motor into linear motion, which is needed to move the window up or down.
- Moving the Window: The mechanical energy generated by the motor is used to lift or lower the window glass. Cables or linkages provide the necessary force to overcome gravity and friction, allowing the window to move smoothly.
- Safety Features: In modern power window systems, sensors may continuously monitor the window’s position. If an obstruction is detected, such as a hand or an object in the window’s path, the sensor sends a signal to the control module, which reverses the motor’s direction. This process is based on the principle of detecting changes in electrical resistance or other sensor technologies.
- Controlled Speed: The science of control engineering is applied to ensure that the window moves at a controlled speed. This prevents abrupt or jarring movements that could cause discomfort or damage.
- Reaching the Desired Position: The window regulator continues to operate until the window reaches the desired position. This is achieved through a combination of precise mechanical design, electrical control, and feedback from position sensors.
- Safety and Durability: Throughout the entire process, materials and components are carefully selected and engineered to ensure the safety and durability of the window regulator system, even under challenging conditions.
Conclusion:
The science behind window regulator operation is a testament to the integration of mechanical engineering, electrical systems, and materials science in modern vehicles. Whether you have manual or power windows, understanding the principles at work behind this seemingly simple convenience can give you a greater appreciation for the engineering excellence that goes into making your daily drive more comfortable and enjoyable. So, the next time you effortlessly open or close your car window, remember the fascinating science behind this everyday feat of automotive technology.